ICU Management & Practice, Volume 17 - Issue 4, 2017
Development and evaluation of a module as part of an undergraduate international honours degree programme
Preparing undergraduate
students for the complex and daunting environment of the intensive care unit
(ICU) is difficult for most undergraduate programmes. The European School of
Physiotherapy, Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences, offers an international
undergraduate programme for students preparing to work anywhere in the world.
To prepare these students for ICU, the ICU course includes, besides a clinical
rotation, an evidence-based e-learning module. Students and international ICU
clinicians helped evaluate the content and didactics of the module. This
article reports on the development and results of the first round of this
evaluation.
Physiotherapy
practice in the intensive care unit (ICU) requires highly specialist skills and
knowledge, but no specific requirements are described in the physiotherapeutic
competence profile (Gosselink et al. 2008). Recently, several initiatives have
been developed and published with the aim to establish minimum clinical
standards for the ICU physiotherapist (Skinner et al. 2016; Van Aswegen et al.
2017; Hanekom et al. 2015). However, as yet, no formal postgraduate training is
required or available for physiotherapists (PTs) starting to work in ICU.
Undergraduate programmes are expected to prepare graduates for any clinical
environment, including the complex ICU setting. The undergraduate programme of
the European School of Physiotherapy (ESP) is an international BSc (Hons)
programme as part of the Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences in Amsterdam,
the Netherlands. Currently students from 42 nationalities are enrolled in the
programme. The majority of the students will return to work in their home
country after graduation. It is the aim of the programme to prepare graduates
as much as possible for clinical work in any international environment. This
poses challenges as well, as clinical ICU work and expectations of the
physiotherapist in ICU, for example, differ per country and sometimes even per
hospital.
You might also like:Physiotherapy services in the Australian ICU
Such expectations consist generally of having a strong theoretical foundation, awareness of safety criteria, possessing skills and knowledge with regards to ICU-specific physiotherapeutic assessment and interventions, and having had practical experience. To provide students with skills and knowledge required for working in intensive care, an ICU course was added in 2016 as a compulsory part of our undergraduate programme. We developed an evidence-based e-learning module as a prerequisite for the student's clinical rotation.
The aim of the project described here was to evaluate the feasibility of e-learning as a teaching method and students' satisfaction with the content and user-friendliness of the ICU e-learning module.
Development of the module
The e-learning module was developed in close collaboration with clinical and research experts of the rehabilitation department of the Academic Medical Center (AMC) in Amsterdam. The ICU department in the AMC is the location where most of the course's videos were taped. The module was piloted among a group of students, didactic and clinical experts during two 6-week periods in 2015 and 2016. Feedback was used for a final revision to the module, before incorporation in the curriculum.
Content of the e-learning module
The
e-learning consists of 7 modules, related to the general environment of ICU and
specific ICU equipment, impact of ICU stay on the patient and family, physiotherapy
assessment and interventions, and multidisciplinary collaboration. Through a
variety of teaching methods, such as interactive assignments, videos, scientific
articles and quizzes the content is brought to the students in a 6-week online
course.
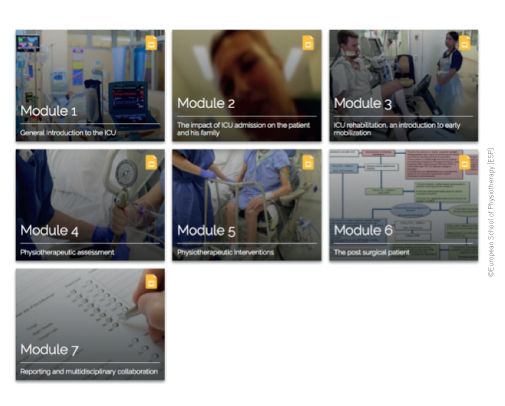
Figure 1. Overview modules e-learning 'Physiotherapy in the ICU'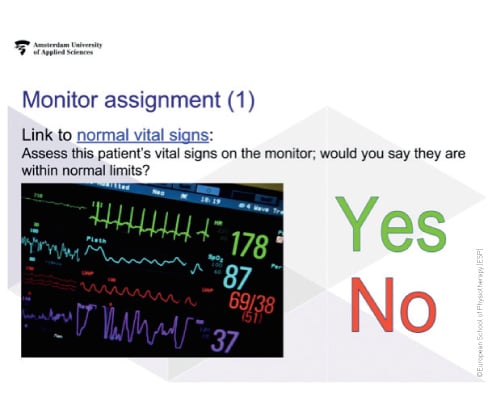
Figure 2. Example assignment
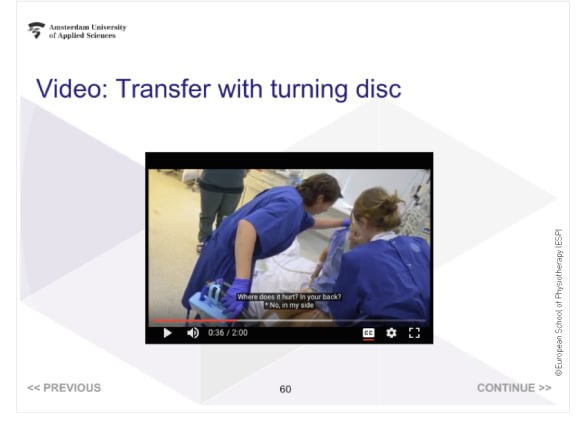
Figure 3. Example video
Methods of evaluation
The e-learning module's evaluation forms part of a larger PhD research project on rehabilitation after critical illness. Several groups of ESP students conducted their bachelor thesis research within this PhD research project.
In a first round of evaluations (during September-December 2016), when the module was piloted, focus group meetings and semi-structured interviews were held to obtain information on usefulness and user-friendliness of the e-learning. The written test was analysed for constructive alignment with the course objectives.
Results
Undergraduate students evaluated the ICU e-learning's content as very posi tive and an important contribution to the existing curriculum. Students highlighted the value of the practical videos taped in the ICU department of the AMC as well as the interactive and the diverse assignments.
Students felt that the content of the e-learning prepared them sufficiently for the physiotherapeutic tasks expected of students during their clinical rotation in ICU, as well as the assessment of safety criteria for early mobilisation (Sommers et al. 2015).
Analysis of the exam questions and results led to revision of the exam, with a larger focus on the application of clinical reasoning skills.
The feedback rounds resulted in many suggestions regarding user-friendliness of the e-learning environment and technical problems encountered during the pilot phase. This resulted in major technical revisions to the module.
Further development
In a second round of evaluations (during September-December 2017), focus group meetings with students who completed both the theoretical (e-learning) as well as the practical part of the ICU course will be conducted. Interview rounds with ICU clinicians from several international and ICU settings will be planned. Whereas the focus for the first round of evaluations was on evaluation of user-friendliness and accessibility of the module, the second round evaluation's focus is on appropriateness and completeness of the content with regards to the (international) ICU environment. Based on results of these evaluations the e-learning module will be adjusted.
Conclusion
Our study concludes that an e-learning module on physiotherapy in the ICU is a feasible method to provide students with the basic knowledge, skills and clinical reasoning required for a clinical rotation in the ICU setting.
The e-learning is meant to be complementary to the practical observation and as such the content is found very useful for students just before or during their clinical rotation.
References:
Van Aswegen H, Patman S, Plani N et al (2017) Developing minimum clinical standards for physiotherapy in South African ICUs: A qualitative study. J Eval Clin Pract, 0: 1-8. doi: 10.1111/ jep.12774 [Epub ahead of print]










