HealthManagement, Volume 24 - Issue 3, 2024
Organisational culture has a pivotal impact on M&A success. Neglecting cultural differences can lead to reduced productivity, operational hurdles, and strategic misalignments. Proactive strategies like cultural assessments and effective communication foster integration and enhance overall merger outcomes in a competitive business landscape.
Key Points
- Importance of Organizational Culture: Organizational culture significantly impacts M&A success, influencing decision-making, communication, and conflict management within merged entities.
- Challenges in M&A Processes: Cultural differences often overlooked in M&A can lead to integration failures, decreased morale, and inefficiencies, jeopardising overall performance.
- Strategic Alignment of Cultural Elements: Successful mergers require strategic alignment of leadership styles, values, and communication practices to foster a cohesive environment.
- Critical Areas for Attention: Effective integration strategies should address differences in leadership styles, culture, values, communication, and diversity and inclusion practices.
- Consequences of Ignoring Cultural Differences: Neglecting cultural differences can result in reduced productivity, operational disruptions, strategic misalignments, and increased employee turnover, highlighting the need for proactive cultural management in M&A processes.
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are common business strategies for achieving growth, diversification, and competitive advantage. While considerable emphasis is placed on financial, legal, and operational aspects, cultural differences often do not receive the necessary attention. Ignoring organisational culture can lead to integration failures, affecting employee morale and, ultimately, the performance of the merged entity. This article explores the unaddressed cultural differences in M&A processes and their impact on successful integration.
M&A Activity Continues in Digital Economy Despite World Uncertainties
Currently, we are living in a BANI[1] world, dominated by turbulences and uncertainties still clouding the outlook for 2024: economic volatility, high inflation rates, geopolitical tensions (including wars), increased regulatory pressure, supply chain disruptions, and upcoming electoral processes in several countries that require navigating uncertainty related to M&A processes.
Despite this situation, now more than ever, the Digital Economy speeds up the process of the creation of value. According to IDC, the IT expenses in Europe in 2024 will grow 2.5 times faster than the GDP to speed up the process of efficient technology in creating value, and 44% of CEOs are aligning both IT and business strategy to speed up the transformation journey. In this context, 70% of executives expect to use M&A operations to accelerate access to technology and related processes, and 60% of CEOs anticipate making at least one acquisition in the next three years to prepare their business for the future (PWC, 2024).
The Crucial Role of Organisational Culture in M&A Success
However, while we see M&A processes governed by financial, legal, and operational aspects, we often overlook the impact of organisational culture. This refers to the shared values, beliefs, norms, and practices that define behaviour within a company. It is an intangible but crucial factor that affects how decisions are made, how employees communicate, and how conflicts are managed. In a merger process, two different organisational cultures must coexist and eventually integrate. If not handled properly, it can lead to a disastrous failure of the integration. The clash of cultures can result in misalignment of goals, loss of key talent, decreased morale, and overall inefficiency. Successful mergers require a deep understanding and strategic alignment of cultural elements to foster a cohesive and productive environment. Therefore, recognising and addressing cultural differences early in the M&A process is essential for ensuring a smooth transition and realising the intended synergies and benefits of the merger.
Addressing Cultural Differences in M&A: Leadership Style, Culture & Values
Leadership style and values occupy a prime position among the main cultural differences that can arise in an M&A process. However, strategies can be applied to mitigate a potential negative impact.
- Leadership styles: Having different leadership styles (for example, authoritarian and hierarchical vs. horizontal and collaborative) can lead to tension and confusion among employees who may be unsure of whom to report to or how decisions are made.
- Culture, values, and beliefs: An organisation's fundamental values and beliefs influence its culture. For example, one company may prioritise innovation and risk-taking, while another may focus on stability and risk minimisation. Aligning values and beliefs is essential for successful integration, as discrepancies can lead to resistance and conflicts. In this regard, it is interesting to analyse the differences in innovation.
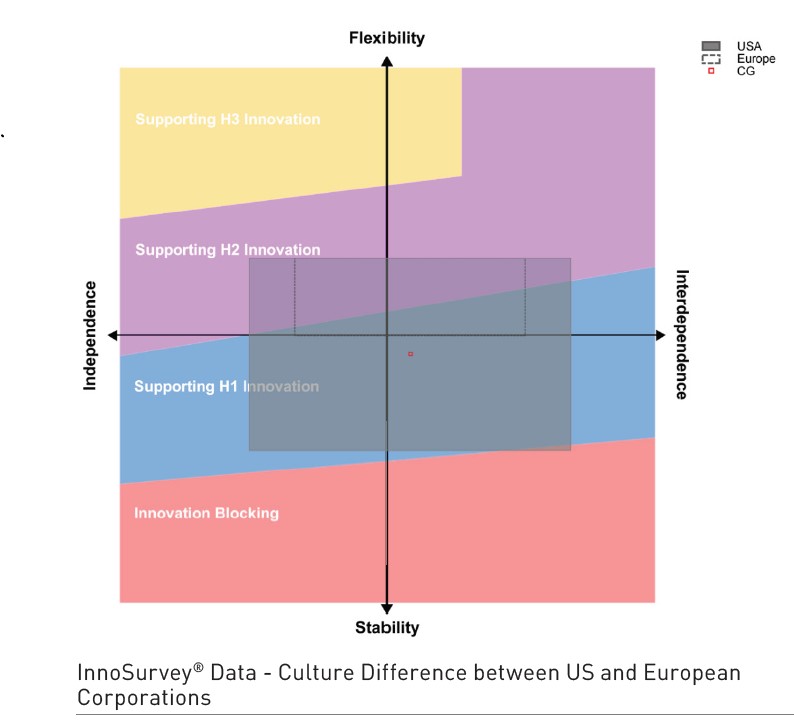
Cultural integration efforts require continuous monitoring and willingness to adapt strategies based on feedback and evolving circumstances. As seen from the Culture Mapping taken from InnoSurvey®, containing global data of more than 5000 companies from 105 countries, we can see the culture gap between US corporations and European corporations. It shows that US companies with a broader culture map can easily encompass a European company acquisition. In contrast, the other way around, European companies have to make significant changes management in place to overcome the culture gap.
Understanding and addressing cultural differences is essential for the success of M&A initiatives. Companies can enhance integration, employee engagement, and overall performance by proactively managing these differences.
Addressing Cultural Differences in M&A: Communication, Diversity & Inclusion
Two other critical areas that require careful attention are communication and D&I. These elements significantly influence how well the merged entities can function as a cohesive unit and achieve their strategic goals.
- Communication (both internal and external). The way information is conveyed both inside and outside the company is another critical cultural aspect. Some organisations prefer formal and structured communication, while others opt for a more informal and open communication style. Differences in communication styles can lead to misunderstandings and a lack of transparency during the integration process.
- Diversity and inclusion. The approach to diversity and inclusion may be different in organisations, even if both promote an inclusive environment. Alignment in diversity policy can be crucial to avoid tensions and promote an inclusive work environment.
Impact & Consequences of Ignoring Cultural Differences in M&A Integration
When cultural differences are not adequately addressed, the consequences can be significant, especially in the following areas:
- Reduced morale and productivity, leading to conflicts and misunderstandings, which affect employee morale and productivity. In addition, it can increase the resistance to change by employees who may resist new policies, processes, or management styles introduced by the acquiring company.
Now more than ever, companies are focused on employee productivity. An increase in layoffs, especially in overlapping roles and voluntary departures, due to uncertainty and dissatisfaction with the new management can prompt valuable employees to leave, increasing employee rotation.
- Failures in operational integration. Differences in practices, systems, and processes can hinder operational integration, affecting the efficiency and effectiveness of the new entity. Also, organisational structure, roles, and responsibilities can create confusion and inefficiencies.
- Strategic misalignments. Misalignment of strategic visions and goals between merging entities can lead to conflicts and diluted focus, which increases execution risks (divergence in execution styles and priorities can hinder the realisation of synergies and intended benefits).
Conclusion
Mergers and acquisitions offer corporations significant strategic benefits, such as market expansion, increased innovation capabilities, and economies of scale. However, cultural differences in mergers and acquisitions are a decisive factor that should not be ignored. Addressing these differences proactively and strategically can be the key to successful integration. By recognising the importance of organisational culture and taking steps to align differences, companies can maximise opportunities for long-term growth and success.
To help organisations address cultural differences, conducting a cultural assessment before the merger or acquisition (through interviews, surveys, and/or document analysis to understand organisational cultures) is essential. This will identify differences between the organisations and allow for the planning of appropriate integration strategies.
Additionally, maintaining open and transparent communication throughout the integration process will better inform employees about changes, objectives, and expectations, thereby reducing uncertainty and fostering collaboration.
Finally, it is crucial to implement cultural integration programmes that help align differences between both organisations. Workshops, training sessions, or team-building activities will promote cohesion among employees from both organisations.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References:
PwC Spain (2024) Tendencias globales de la industria de M&A en 2024. La reactivación del mercado de M&A ha empezado. ¿Estás preparado? Available at: https://www.pwc.es/es/deals/global-m-y-a-industry-trends-2024.html





