
Due to an aging population, the number of Total Knee Arthroplasties (TKA) keeps increasing. Despite significant efforts, progress is still needed to improve the outcome of the current 20% of patients who are not satisfied with their surgical results.8
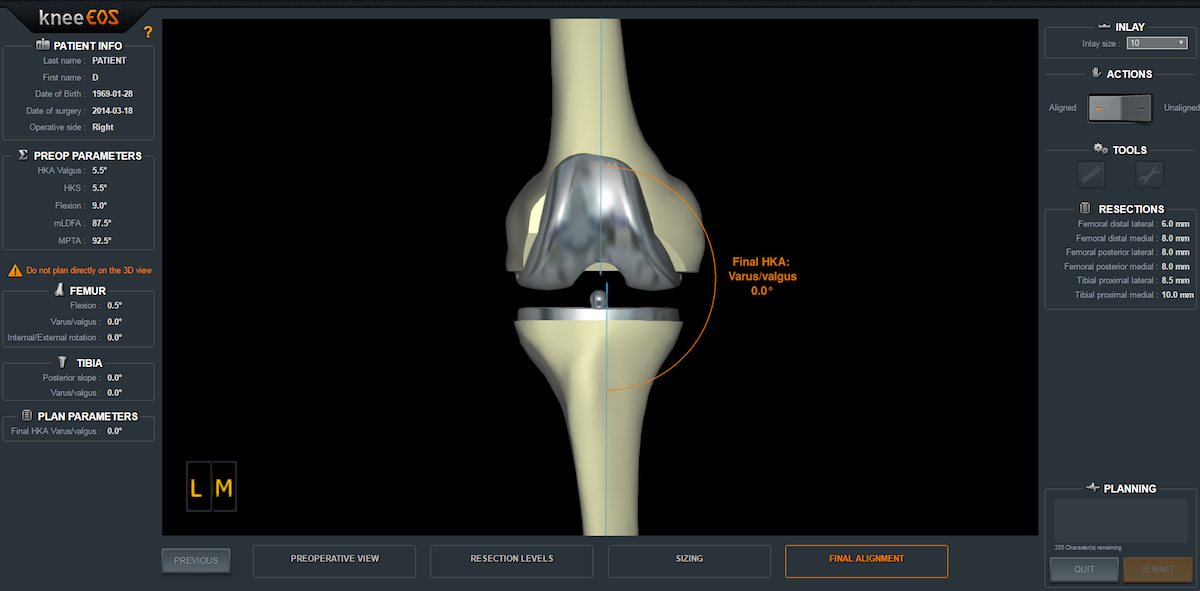
The kneeEOS online software is used to plan a primary, total knee arthroplasty by automatically selecting and positioning implants in 3D. The surgeon can modify the plan with immediate feedback on how changes to the plan affect relevant clinical parameters in 3D.
Thanks to the full body, weight-bearing 3D EOS images, kneeEOS can be used to anticipate the consequences of the prosthesis placement on leg alignment and knee rotation; two key criteria for successful total knee arthroplasties.
Clinical benefits
- Patient-matched implant size selection without complex radiological calibration protocols
- Unique 3D planning for implant positioning, including the resection levels on the femur and the tibia, without the need for additional CT exams
- Real-time 3D surgical simulations of the impact on leg alignment (HKA) and knee rotations (varus/valgus, flexion/extension, internal/external rotation) in a functional position
Facility-wide efficiency
- Automatic proposal of implant size and position according to the 2D/3D patient data set
- Online database of 3D implants from multiple manufacturers
- Online access from any computer through a compliant server
- Customizable, patient-specific planning reports
Bibliography
- Comparison of radiation dose, workflow, patient comfort and financial break-even of standard digital radiography and a novel biplanar low-dose X-ray system for upright full-length lower limb and whole spine radiography. Dietrich TJ et al. Skeletal Radiol. 2013.
- Diagnostic imaging of Spinal deformities: Reducing Patients Radiation Dose With a New Slot-Scanning X-ray Imager. Deschenes S, Charron G, Beaudoin G,Labelle H, Dubois J, Miron M, Parent S. Spine April 2010, 35 (9): 989. .
- Ionizing radiation doses during lower limb torsion and anteversion measurements by EOS stereoradiography and computed tomography. Delin C et al. Eur J Radiol. 2014
- EOS microdose protocol for the radiological follow-up of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Ilharreborde B. et al. Eur Spine J. 2015
- Preoperative three-dimensional planning of total hip arthroplasty based on biplanar low-dose radiographs: accuracy and reproducibility for a set of 31 patients. Mainard, D et al. Communication at ISTA 2014.
- The EOS imaging system and its uses in daily orthopaedic practice. Illes T, Somoskeoy S. Int Orthop2012 Feb 28.
- Accuracy of Digital Preoperative Templating in 100 Consecutive Uncemented Total Hip Arthroplasties, Journal of Arthroplasty, 2013-02-01, R.Shaarani & al
- What proportion of patients report long-term pain after total hip or knee replacement for osteoarthritis? A systematic review of prospective studies in unselected patients. Beswick, A. D., V. Wylde, R. Gooberman-Hill, A. Blom and P. Dieppe (2012). BMJ Open.
- Meijjo Hospital, Nagoya, Japan
More products from this supplier
- United States
- United States
- United States
- United States
- United States
- United States
- United States
Loading...









