ICU Management & Practice, Volume 19 - Issue 3, 2019
Who Should be Nourished?
When and How?
Pharmaconutriments
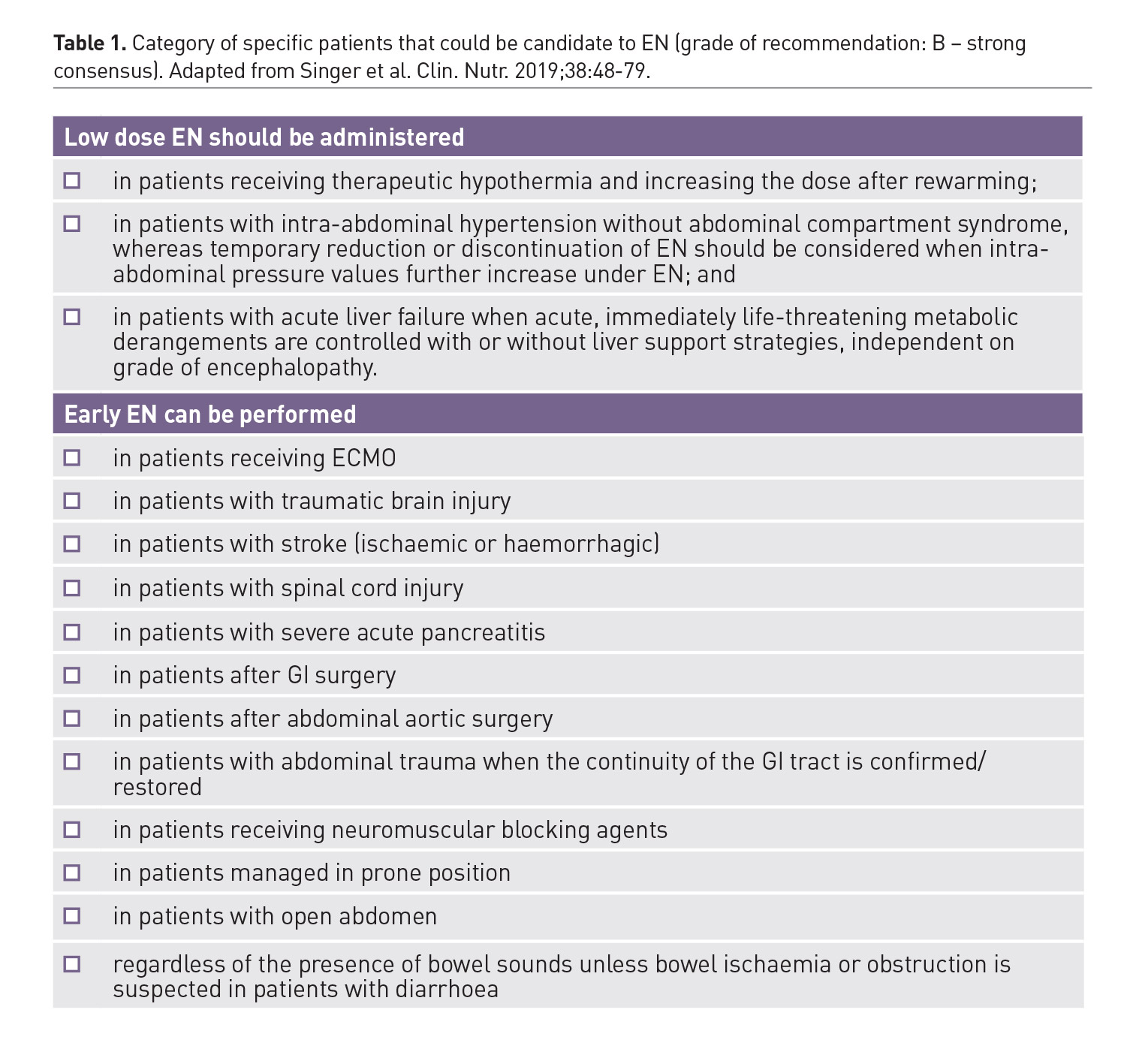
Specific Conditions
Future
Key Points
- Patients admitted to the ICU and staying more than 48h are at nutritional risk and deserve particular attention.
- Enteral route is still recommended when there is no contraindication.
- When the enteral route is not available, a parenteral nutrition should be implemented at a later stage.
- Hypocaloric nutrition is preferred over isocaloric nutrition for the first week of ICU stay.
- A new indirect calorimeter that is light, easily mobillised, with easy calibration process, equipped with a friendly touch screen and interface and that is reliable was recently released.
Abbreviations
Conflicts of Interest
References:
Alberda C, Gramlich L, Jones N, Jeejeebhoy K, Day AG, Dhaliwal R, Heyland DK (2009) The relationship between nutritional intake and clinical outcomes in critically ill patients: results of an international multicenter observational study. Intensive Care Med, 35:1728-1737.
Allingstrup MJ, Kondrup J, Wiis J, Claudius C, Pedersen UG, Hein-Rasmussen R, Bjerregaard, MR, Steensen M, Jensen TH, Lange T, Madsen MB, Møller MH, Perner A (2017) Early goal-directed nutrition versus standard of care in adult intensive care patients: the single-centre, randomised, outcome assessor-blinded EAT-ICU trial. Intensive Care Med, 43:1637-1647.
Amrein K, Schnedl C, Holl A, Riedl R, Christopher KB,
Pachler C, Urbanic Purkart T, Waltensdorfer A, Munch A,
Warnkross H, Stojakovic T, Bisping E, Toller W, Smolle KH,
Berghold A, Pieber TR, Dobnig H (2014) Effect of HighDose Vitamin D3 on Hospital Length of Stay in Critically
Ill Patients With Vitamin D Deficiency: The VITdAL-ICU
Randomized Clinical Trial .JAMA, 312 1520-1530.
Arabi YM, Aldawood AS, Haddad SH et al. (2015) Permissive Underfeeding or Standard Enteral Feeding in Critically Ill Adults. N Engl J Med, 372:2398-2408.
Arabi, YM, Casaer MP, Chapman M,et al. (2017) The intensive care medicine research agenda in nutrition and metabolism. Intensive Care Med, 43:1239-1256.
Bendavid I, Singer P, Theilla M et al. (2017) NutritionDay ICU: A 7 year worldwide prevalence study of nutrition practice in intensive care. Clin Nutr, 36:1122-1129.
Berger MM, Reintam-Blaser A, Calder PC et al. (2019) Monitoring nutrition in the ICU. Clin Nutr, 38:584-593.
Casaer MP, Mesotten D, Hermans G et al. (2011) Early versus late parenteral nutrition in critically ill adults. N Engl J Med, 365, 506-517.
Casaer MP, Wilmer A, Hermans G et al. (2013) Role of disease and macronutrient dose in the randomized controlled EPaNIC trial: a post hoc analysis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 187:247-255.
Doig, G.S., Simpson, F., Heighes, P.T., Bellomo, R., Chesher, D., Caterson, I.D., Reade, M.C., Harrigan, P.W. & Refeeding, S.T.I.G. (2015) Restricted versus continued standard caloric intake during the management of refeeding syndrome in critically ill adults: a randomised, parallel-group, multicentre, single-blind controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med, 3, 943-952.
Doig, G.S., Simpson, F., Sweetman, E.A., Finfer, S.R., Cooper, D.J., Heighes, P.T., Davies, A.R., O’Leary, M., Solano, T. & Peake, S. (2013) Early parenteral nutrition in critically ill patients with short-term relative contraindications to early enteral nutrition: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA, 309, 2130-2138.
Fetterplace, K., Deane, A.M., Tierney, A., Beach, L.J., Knight, L.D., Presneill, J., Rechnitzer, T., Forsyth, A., Gill, B.M.T., Mourtzakis, M. & MacIsaac, C. (2018) Targeted Full Energy and Protein Delivery in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial (FEED Trial). JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr, 42, 1252-1262.
Fraipont, V. & Preiser, J.C. (2013) Energy Estimation and Measurement in Critically Ill Patients. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr, 37, 705-713.
Harvey, S.E., Parrott, F., Harrison, D.A., Bear, D.E., Segaran, E., Beale, R., Bellingan, G., Leonard, R., Mythen, M.G., Rowan, K.M. & CALORIES, Trial Investigators (2014) Trial of the Route of Early Nutritional Support in Critically Ill Adults. N Engl J Med, 371, 1673-1684.
Heidegger, C.P., Berger, M.M., Graf, S., Zingg, W., Darmon, P., Costanza, M.C., Thibault, R. & Pichard, C. (2013) Optimisation of energy provision with supplemental parenteral nutrition in critically ill patients: a randomised controlled clinical trial. Lancet, 381, 385-393.
Koekkoek, W.A.C.K., van Setten, C.H.C., Olthof, L.E., Kars, J.C.N.H. & van Zanten, A.R.H. (2019) Timing of PROTein INtake and clinical outcomes of adult critically ill patients on prolonged mechanical VENTilation: The PROTINVENT retrospective study. Clin Nutr, 38, 883-890.
McCarthy, M.S., Warren, M. & Roberts, P.R. (2016) Recent Critical Care Nutrition Trials and the Revised Guidelines: Do They Reconcile. Nutr Clin Pract, 31, 150-154.
McClave, S.A., Taylor, B.E., Martindale, R.G., et al.. (2016) Guidelines for the Provision and Assessment of Nutrition Support Therapy in the Adult Critically Ill Patient: Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) and American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.). JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr, 40, 159-211.
Oshima, T., Berger, M.M., De Waele, E., Guttormsen, A.B., Heidegger, C.P., Hiesmayr, M., Singer, P., Wernerman, J. & Pichard, C. (2017a) Indirect calorimetry in nutritional therapy. A position paper by the ICALIC study group. Clin Nutr, 36, 651-662.
Oshima, T., Ragusa, M., Graf, S., Dupertuis, Y.M., Heidegger, C.P. & Pichard, C. (2017b) Methods to validate the accuracy of an indirect calorimeter in the in-vitro setting. Clin Nutr ESPEN, 22, 71-75.
Patel, J.J., Lemieux, M., McClave, S.A., Martindale, R.G., Hurt, R.T. & Heyland, D.K. (2017) Critical Care Nutrition Support Best Practices: Key Differences Between Canadian and American Guidelines. Nutr Clin Pract, 32, 633-644.
Peake, S.L., Davies, A.R., Deane, A.M., Lange, K., Moran, J.L., O’Connor, S.N., Ridley, E.J., Williams, P.J. & Chapman, M.J. (2014) Use of a concentrated enteral nutrition solution to increase calorie delivery to critically ill patients: a randomized, double-blind, clinical trial. Am J Clin Nutr, 100, 616-625.
Preiser, J.C. (2018) High protein intake during the early phase of critical illness: yes or no. Crit Care, 22, 261.
Preiser, J.C., van Zanten, A.R., Berger, M.M et al. (2015) Metabolic and nutritional support of critically ill patients: consensus and controversies. Crit Care, 19, 35.
Preiser, J.C. & Wernerman, J. (2017) Provision of Nutrients to the Acutely Ill. Introducing the “Baby Stomach” Concept. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 196, 1089-1090.
Rattanachaiwong, S. & Singer, P. (2019) Indirect calorimetry as point of care testing. Clin Nutr,
Reignier, J., Boisramé-Helms, J.,
Brisard et al.. (2018) Enteral versus parenteral early
nutrition in ventilated adults with shock: a randomised, controlled,
multicentre, open-label, parallel-group study (NUTRIREA-2). Lancet, 391, 133-143.
Reintam Blaser, A. & Berger, M.M. (2017) Early or Late Feeding after ICU Admission. Nutrients, 9, 1278.
Reintam Blaser, A., Starkopf, J., Alhazzani, W. et al. (2017) Early enteral nutrition in critically ill patients: ESICM clinical practice guidelines. Intensive Care Med, 43, 380-398.
Rice, T.W., Mogan, S., Hays, M.A., Bernard, G.R., Jensen, G.L. & Wheeler, A.P. (2011) Randomized trial of initial trophic versus full-energy enteral nutrition in mechanically ventilated patients with acute respiratory failure. Crit Care Med, 39, 967-974.
Rugeles, S.J., Rueda, J.D., Diaz, C.E. & Rosselli, D. (2013) Hyperproteic hypocaloric enteral nutrition in the critically ill patient: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Indian J Crit Care Med, 17, 343-349.
Schetz, M., De Jong, A., Deane, A.M., Druml, W., Hemelaar, P., Pelosi, P., Pickkers, P., Reintam-Blaser, A., Roberts, J., Sakr, Y. & Jaber, S. (2019) Obesity in the critically ill: a narrative review. Intensive Care Med, 45, 757-769.
Singer, P., Blaser, A.R., Berger, M.M., Alhazzani, W., Calder, P.C., Casaer, M.P., Hiesmayr, M., Mayer, K., Montejo, J.C., Pichard, C., Preiser, J.C., van Zanten, A.R.H., Oczkowski, S., Szczeklik, W. & Bischoff, S.C. (2019) ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in the intensive care unit. Clin Nutr, 38, 48-79.
Singer, P., Anbar, R., Cohen, J., Shapiro, H., Shalita-Chesner, M., Lev, S., Grozovski, E., Theilla, M., Frishman, S. & Madar, Z. (2011) The tight calorie control study (TICACOS): a prospective, randomized, controlled pilot study of nutritional support in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med, 37, 601-609.
Villet, S., Chiolero, R.L., Bollmann, M.D., Revelly, J.P., Cayeux, R.N.M., Delarue, J. & Berger, M.M. (2005) Negative impact of hypocaloric feeding and energy balance on clinical outcome in ICU patients. Clin.Nutr., 24, 502-509.
Weijs, P.J.M. (2018) Route, early or energy? Protein improves protein balance in critically ill patients. Crit Care, 22, 91.
Zuercher, P., Moret, C.S., Dziewas, R. & Schefold, J.C. (2019) Dysphagia in the intensive care unit: epidemiology, mechanisms, and clinical management. Crit Care, 23, 103.
Zusman, O., Theilla, M., Cohen, J., Kagan, I., Bendavid, I. & Singer, P. (2016) Resting energy expenditure, calorie and protein consumption in critically ill patients: a retrospective cohort study. Crit Care, 20, 367.








