Executive Summary
Cancer care is becoming increasingly
complex and personalized. More and more
patient characteristics and disease specific
data – clinical history, comorbidities,
imaging, laboratory data, genomics/
proteomics, lifestyle factors, pathology
results – have to be factored in when
deciding on diagnostic measures and
care pathways. The most recent treatment
recommendations can be found in international guidelines that, in the case
of prostate cancer, are updated up to
twice a year.
Together with Siemens Healthineers,
University Hospital Basel (USB) has decided
to collaborate on and implement AI-Pathway
Companion Prostate Cancer, a next-generation clinical decision support software.
AI-Pathway Companion is CE-certified1 and
uses AI-technologies to generate evidence based recommendations for urologists who
treat prostate cancer patients and have to
decide on the optimal treatment approach.
The software presents a clinical navigation
map that is both standardized2 and highly
personalized. It supports the physician by
providing – at the point of care – a readily
accessible overview of the patient’s clinical
condition and diagnostic and therapeutic
options at any given moment3. Furthermore,
it helps the patient by illustrating the disease
progression over time and possible disease
trajectories based on therapy decision.
For Siemens Healthineers, advancing artificial
intelligence and making it ready for clinical
use is an important component of its strategy
2025, and AI-Pathway Companion is one of
the solutions to drive new business beyond
radiology and to fortify its position as a trailblazer in digital healthcare. It builds on the
company’s strong product portfolio, but even
more so on the profound knowledge of clinical
processes and evidence-based care along
the care pathway that Siemens Healthineers
has acquired in more than a century of being
a healthcare innovation leader.
“It is always helpful to have knowledge
available at the point of care,
and it
is very helpful for clinicians to see
patient-specific decision trees unfold.”
Professor Philip Cornford4
Cancer Lead at Royal Liverpool University Hospitals Trust,
Vice Chair European Association of Urology (EAU)
Prostate Cancer Guideline Panel
At USB, AI-Pathway Companion was piloted
successfully, and it is now being used in
clinical routine to improve the efficiency of
the multidisciplinary workflows of diagnosing
and treating patients with adenocarcinoma,
the most common form of prostate cancer.
The vision is that of a digital, transparent, and
highly personalized information-sharing and
decision-making platform that draws both on
published evidence and real-life patient data.
Guideline adherence and clinical decision support
In cancer care, treatment standards are usually
summarized and referenced in national and
international guidelines, notably the guidelines
of the US National Comprehensive Cancer
Network (NCCN) that radiate way beyond
North America. In urological cancers like
prostate cancer, they are referenced in the
guidelines of the European Association of
Urology (EAU) which, again, are adopted by
many healthcare systems outside of Europe.
“Every patient with prostate cancer
has the right to be treated according
to the most recent evidence-based
recommendations.”
Prof. Helge Seifert4
Head of the Department of Urology
at University Hospital Basel
It has repeatedly been demonstrated that
guideline adherence in oncology translates
into better outcomes. For example, a German
breast cancer analysis showed that guideline
adherence strongly predicted relapse-free
survival and overall survival regardless of prognostic index. [1] A very recent breast cancer
study from Asia clearly correlated survival with
guideline adherence for different types of
treatment, specifically surgery, chemotherapy,
radiotherapy, and endocrine therapy. [2] And a
further analysis based on a US national dataset
showed that adherence to American College
of Surgeons recommendations improved breast
cancer survival. [3]
While most data on guideline adherence and
patient outcomes refer to breast cancer, data
also exist for other types of cancer that point
in the same direction. In California, guideline
adherence correlated with survival in pancreatic cancer. [4] And in an Italian multi center
study, adherence to EAU guidelines translated
into better overall survival in penile cancer. [5]
Evidence-based care leads to better clinical
outcomes, but how does it affect cost?
A multi-year study performed in association
with professionals from Abramson Cancer
Center of the University of Pennsylvania
and Johns Hopkins Carey Business School
revealed that the cost of unwarranted
components of oncology treatments averaged
$25,579 per patient. At current annual
cancer incidence rates in the US, this translates
to over $10 billion per year in unnecessary
costs that could be significantly reduced
by eliminating unwarranted, non-evidence based cancer treatment. [6]
A further study of women with early-stage
breast cancer who received treatment
for secondary metastases demonstrated
both lower health care utilization and
lower Medicare costs for patients receiving
guideline-concordant care. The study
of 5,651 patients conducted from 2006
to 2013 found that in comparison with
concordant treatments, non-concordant
treatments were associated with $1,765
higher average Medicare costs per month. [7]
Thus, routine use of guidelines will benefit
patients in multiple ways. But with an
abundance of new research publications on
personalized therapies and guideline updates
becoming more and more frequent, acting
according to guidelines is proving increasingly
difficult for physicians, says Professor
Philip Cornford, Vice Chair of the EAU Prostate
Cancer Guideline Panel:
“The EAU Prostate Cancer
Guideline
is updated
every spring, and often
there is an
additional
update in autumn.
Last
year alone there were
4,500 new publications.”
Professor Philip Cornford4
Cancer Lead at Royal Liverpool
University Hospitals Trust,
Vice Chair
European Association of Urology (EAU)
Prostate Cancer Guideline Panel
The medical information tsunami that physicians are facing can be illustrated by numerous
statistics. For example, the doubling time for
medical data was 3.5 years in 2010. In 2020
it is estimated to be just 73 days. [8] As a
result of information overload in an age of
personalized precision medicine, guideline
adoption by physicians providing cancer care
is far from perfect, and there is considerable
variability between institutions.
“What seems clear is that there
are big gaps between what guideline
committees say and what really
happens when a doctor sits in front
of a patient.”
This is where digital clinical decision
support systems come into play. AI-Pathway
Companion optimizes care pathways by
creating a clinical navigation map that
integrates patient-specific data from various
sources. It also generates evidence-based
treatment recommendations by matching
individual patient data to guideline recommendations.
“A digital tool that provides
evidence-based
information in
the context of individual patients
will
likely raise awareness for
guideline recommendations.”
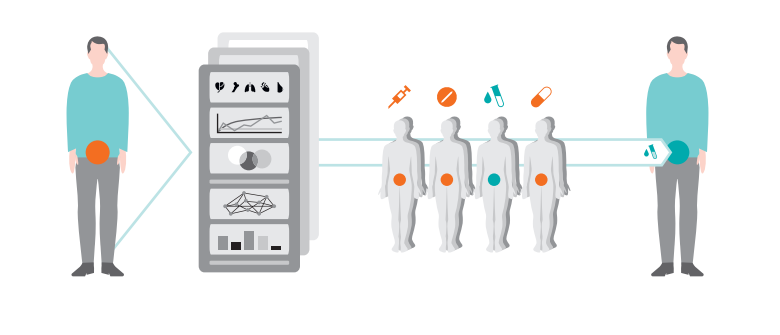
Personalization in detail
AI-Pathway Companion Prostate Cancer
features various tools that provide personalized information or recommendations based
on individual disease history, clinical data,
personal preferences, and stage of disease.
Here are just a few examples:
- Prostate cancer nomograms provide and visualize personalized predictions of disease courses and treatment outcomes. Patients will better understand the nature of their highly individual prostate cancer and the likely outcomes of different therapies.
- Nomograms can also be used to risk stratify patients, specifically in first-line treatment. This helps physicians to put patients on the best possible treatment pathway.
- Several visual dashboards and patient engagement functionalities boost shared decision- making during doctor-patient conversations. Thus equipped, the patient will better understand the different treatment options and the physician’s recommendations and will be more capable of expressing informed preferences.
Personalized predictions
of disease courses through
automatically assembled
prostate cancer nomograms
help the patient to express
informed preferences.
Visualizations like these
can be considered
enablers for genuinely
shared decision-making.
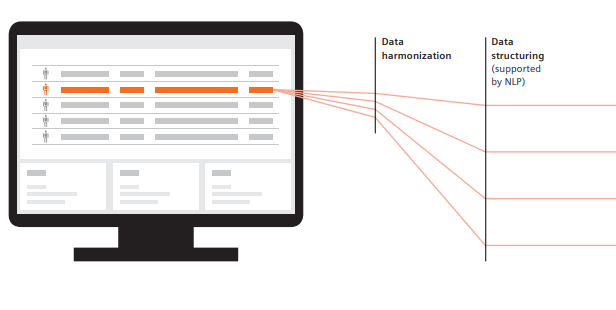
Standardization in detail
Cancer care varies greatly depending on the
institution, indicating that adoption of
evidence-based guidelines could be improved
significantly. [9] This is especially true for prostate cancer: A Dutch analysis of 15 European
treatment recommendations for different types
of cancer showed that there was a particularly
high inter-hospital variation in adherence to
prostate cancer guidelines. [10]
Clinical decision support helps to reduce
variations in care pathways – within an institution, but also across institutions. AI-Pathway
Companion Prostate Cancer contributes to
better standardization and reduced variation
thanks to a number of technical and structural
features and use of AI-technologies. These
features help align individual patient data
points with evidence-based knowledge and
thus assist clinical decision-making:
- Aggregation of disease-specific and relevant information from reports that are stored in disparate IT systems like the electronic medical record (EMR) and the radiological, oncological and laboratory information systems (RIS, OIS, LIS).
- Data is structured as necessary with the help of NLP and visualized along the individual clinical pathway to ensure informed decision-making. For example, radiology and pathology results are correlated and superimposed to provide tumor visualization.
- Customers retain a high flexibility regarding the source of evidence-based information. All diagnostic and therapeutic alternatives that exist in guidelines are featured in AI-Pathway Companion. Institution-specific standard-operating procedures (SOP)6 can be integrated and, with the help of AI-technologies, provided in a standardized fashion when necessary or desired.
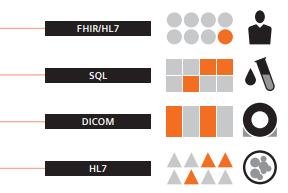
AI-Pathway Companion is technically
interoperable and vendor neutral. It utilizes
common international standards to draw
healthcare data from, and pass data between,
systems. Specifically, the software is FHIR
ready and can also exchange data through
standards like HL7 and DICOM.
An institution that intends to use AI-Pathway
Companion should be able to provide as much
structured clinical data as possible, since not
all information can be extracted with NLP. The
ideal scenario is that clinical data is entered in
a standardized way from the very outset.
What’s in it for customers?
The USB experience
Urologists at University Hospital Basel (USB)
have decided to take evidence-based prostate
cancer treatment to a new level and rise
to the challenge of multidisciplinary tumor
care by accelerating medical progress.
The Department of Urology is the global pilot
site for AI-Pathway Companion Prostate Cancer
and has recently implemented the new
Siemens Healthineers software in routine care.
By leveraging AI-technologies and smart data
integration capabilities, Prof. Helge Seifert and
his team are successfully reducing complexity
and fighting data overload.
“Clinicians were involved in the
development very early on.
The software really mirrors the
specific
requirements of routine
clinical users.”
Christian Wetterauer4
MD and AI-Pathway Companion Project Lead,
Department of Urology
at University Hospital Basel
The Basel urologists are focusing on two main
use cases at the moment: patient consultations
and multidisciplinary team meetings (MDT).
The overall goal is to improve quality of care
both in-house and across the regional prostate
cancer care network that includes a number
of smaller hospitals and urologists in private
practice in Switzerland and Germany.
As a lower-hanging fruit, efficiency gains in
daily routine will be measured. To this end,
a number of key performance indicators (KPI)
such as ‘time to find certain values’, ‘time to
prepare an MDT’, and ‘overall length of time
for presenting and discussing a patient during
an MDT have been defined. These KPIs are
currently being compared to the status quo
ante, and more are under consideration,
for example ‘time to prepare a consultation’
and ‘time to establish the International
Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS)’. Another
promising area for efficiency gains is the
above-mentioned risk stratification through
nomograms. Until now this has required an
online tool; but with AI-Pathway Companion,
nomograms are created automatically and
made immediately available to the urologist.
Use case patient consultations
AI-Pathway Companion Prostate Cancer provides evidence-based, patient-specific support
at the point of care that can be very valuable
during consultations between physicians
and patients. Dr. Christian Wetterauer4,
Project Lead at USB, aims to make AI-Pathway
Companion the primary user interface for
clinicians: “This software can be considered
an educational tool. It is not a black box,
but makes evidence transparent.”
Using AI-Pathway Companion and its visualization features meets the two prime expectations
of every cancer patient simultaneously:
receiving best possible treatment in line with
available standards and guidelines and talking
face-to-face with their doctor
“Software definitely won’t replace
the doctor.
But it helps to make
well-informed,
evidence-based
recommendations,
and it can make
different
treatment options more
transparent.”
Prof. Helge Seifert4
Head of the Department of Urology
at University Hospital Basel
Use case multidisciplinary tumor board
The second important use case for AI-Pathway
Companion Prostate Cancer at USB is the multidisciplinary tumor board (MDTB). The USB
urologists treat about 200 patients with newly
diagnosed prostate cancer per year. Hundreds
more patients are presented during the weekly
MDTB by colleagues from other hospitals in
the vicinity and by ambulatory urologists.
With 15 to 20 patients discussed weekly at
USB, MDTB preparation is a time consuming
task. Dr. Wetterauer states that preparing
a patient for the MDTB takes between 5 and
12 minutes. Discussing the patient with
colleagues takes another 5 minutes on average.
Using AI-Pathway Companion for patient preparation saves considerable time, since it has
all the necessary data already integrated, and
the information is mapped conveniently along
the patient journey in a way that makes it
immediately usable for the MDTB.

During the MDTB, AI-Pathway Companion
with its patient journey visualization and
NLP-powered risk depiction helps to save
time. It also leads to a much more holistic
presentation and helps to make expert
recommendations more transparent.
Diagnostic and therapeutic options can
be illustrated more clearly and clinical
colleagues can join via teleconferencing.
“We don’t have to put together
the information we need manually
before
an MDTB anymore, because
data aggregation
for each patient
happens automatically.
This
should reduce preparation time
considerably,
ideally close to zero.”
Christian Wetterauer4
MD and AI-Pathway Companion Project Lead,
Department of Urology
at University Hospital Basel
The vision to drive improved patient outcomes
AI-Pathway Companion’s ambitious
goal is to improve patient outcomes.
The vision is to:
- reach profound process improvements
- provide easy scalability thanks to a contemporary platform infrastructure
- propel disease-specific knowledge for elaborate and contextualized decision-making
- drive patient engagement and shared decisions
- generate insights
Improving clinical decision-making is a complex
task, and AI-Pathway Companion is taking a stepwise
approach to get there:
.png)
What’s next in AI-powered cancer care?
Here is our short-term working list:
- Deliver additional and valuable insights to drive informed decision-making
- Develop further pathways such as lung and breast cancer6,7
- Strengthen clinical analytics capabilities: assure the physician that a decision is right
- Promote a consultative implementation approach to propel digital maturity at the customer site
- Accentuate patient centricity to promote patient engagement and patient knowledge and to foster shared decision-making
- Visualize Patient Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs)6 and integrate them in the individual patient pathway, indicating quality of care and effectiveness of therapeutic measures over the course of the disease and the different lines of treatment
And what about mid-term?6
- Increase personalization further by considering patient co-morbidities and taking into account the interaction of different care pathways in patients with more than one disease
- Establish digital twins by providing representation of organ functions and advance other types of patient specific modeling
- Empower physicians to simulate outcome scenarios, for example how a patient will likely react to different chemotherapies
- Identify suitable clinical trials with a trial matching feature based on individual patient characteristics, and raise awareness of existing clinical research on the side of the patient and on that of the urologist
- Enable care givers to leverage self-generated evidence powered by cohort models and advanced prediction models
- Activate deep-learning AI-algorithms to leverage full potential of insights generation
- Use the Similar Patient Search to identify patients with a similar stage of disease or biological background to derive the best treatment option or diagnostic step
Summary
AI-Pathway Companion Prostate Cancer is
a next generation, AI-powered data integration
and clinical decision support software.
Because data from various sources is mapped
transparently and intuitively along the patient journey,
“A software like this will lead to better
quality of care.
It will be especially
valuable in peripheral hospitals
and smaller medical institutions with
a high caseload.
We won’t be able
to offer patient care in the future
without integrating evidence-based
knowledge and patient data.”
Prof. Helge Seifert4
Head of the Department of Urology
at University Hospital Basel
routine cancer care becomes far
more efficient. By matching individual patient
data with up-to-date recommendations
and guidelines from NCCN and EAU and, if
applicable, from local SOPs6, adherence to
evidence-based standards in diagnosis and
treatment is promoted and optimal guideline
adherence facilitated. At University Hospital
Basel, the global pilot site for AI-Pathway
Companion Prostate Cancer, physicians benefit
from more streamlined MDTBs and less time
spent on tasks like assembling data and
performing risk assessments4. Furthermore,
available treatment options can be made
transparent to patients so that shared,
informed decision-making becomes a reality.
Ultimately, better informed decision-making
and higher guideline adherence should
translate into improved medical outcomes
for the prostate cancer patient.
References
[1] Kreienberg R et al. Breast 2018; 40:54-9
[2] Ho PJ et al. Scientific Reports 2020; 10:1330
[3] Zhao B et al. J Surg Oncol 2019; 120:148-59
[4] Visser BC et al. HPB 2012; 14:539-47
[5] Cindolo L et al. World J Urol 2019; 37:1649-57
[6] Lowell E. Schnipper et al., JCO 2012 42.8375
[7] Gabrielle B. Roque et al. ACS 2018 21: 4231-4240
[8] University of Iowa, Carver College of Medicine report, 2014
[9] LeVasseur et al. Current Oncology 2018; 25(4): 263-64
[10] Heins M et al. Eur J Public Health 2017; 27:616-20
The statements by Siemens Healthineers’ customers described herein are
based on results that were achieved in the customer’s unique setting. Because
there is no “typical” hospital or laboratory and many variables exist (e.g.,
hospital size, samples mix, case mix, level of IT and/or automation adoption)
there can be no guarantee that other customers will achieve the same results
1 AI-Pathway Companion Prostate Cancer is CE-compliant in accordance
with Directive 93/42/EEC.
2 AI-Pathway Companion Prostate Cancer VA10A supports EAU and
NCCN guidelines.
3 Prerequisite: All data is available as required per guideline.
Feature dependent on quality of input data.
4 Employed by an institution that receives financial support from
Siemens Healthineers for collaborations.
5 AI-Pathway Companion Prostate Cancer VA10A supports prostate
cancer adenocarcinoma cases only.
6 The features mentioned herein are under development and not
commercially available. Their future availability cannot be ensured.
7 This product is under development and not commercially available.
Its future availability cannot be ensured.
Latest Articles
Siemens, prostate cancer, Decision Support, Quality of Care, clinical decision support, Siemens Healthineers, CDSS, Clinical Decision Support System, multidisciplinary tumor board (MDTB)
Cancer care is becoming increasingly complex and personalized. More and more patient characteristics and disease specific data – clinical history, com...








