Image by Freepik
Hair loss, or alopecia, can be a depressing and distressing condition, affecting one's self-esteem and psychological well-being. Looking for effective treatments has led to many options, ranging from over-the-counter remedies to surgical interventions.
With several options available, how do you know what works best?
Understanding Hair Loss and Its Causes
Understanding the underlying causes is the best approach to exploring treatment options, as they dictate the most effective treatment approach. Here are some of the common causes of hair loss:
Genetic factors
The most common culprit of hair loss is androgenetic alopecia. This condition is mainly hereditary and involves the influence of androgens (hormones) on the hair follicles. In those genetically predisposed, certain hair follicles are sensitive to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of the hormone testosterone.
DHT binds to receptors in the scalp's hair follicles, causing them to shrink or 'miniaturise.' This results in a shorter life span for hair and the production of thinner, shorter hairs with each growth cycle.
Hormonal changes
Apart from genetics, hormonal changes can also lead to hair loss. This is particularly evident in women during events such as pregnancy or childbirth.
Postpartum hair loss, occurring in 90% of women, is a condition caused by declining estrogen levels after giving birth. Similarly, both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism are linked to hair thinning and can affect both men and women.
Medical conditions
Various conditions can lead to hair loss as a secondary symptom. An autoimmune disorder, alopecia areata, stimulates the immune system to attack hair follicles, which manifests as patchy hair loss. This condition affects 2% of the population.
Scalp infections like ringworm can invade the scalp, leading to scaly patches and eventual hair loss. Other systemic conditions, such as lupus, can also lead to hair loss as part of their symptom spectrum.
Lifestyle influences
Lifestyle factors can exacerbate or even trigger hair loss. Nutritional deficiencies--particularly in iron, protein, and vitamins--can lead to hair shedding.
Both physical and emotional stress can precipitate hair loss through a phenomenon known as telogen effluvium. In this instance, stress forces hair follicles into a resting phase, skipping the growth phase and leading to shedding.
Hairstyling practices that pull the hair (like tight braids or ponytails) or harsh chemical treatments can cause traction alopecia, leading to hair breakage and loss.
Hair Loss Treatments and Their Efficacy
Image by Freepik
Examining the science behind each treatment makes it easier to decide on what treatment to choose. Here are the common hair loss treatments:
Minoxidil
Minoxidil is one of the first lines of defence against hair loss. It's available over-the-counter as a topical solution or foam.
Minoxidil works by widening blood vessels and activating potassium channels, which allows more oxygen, blood, and nutrients to the hair follicle. This can prolong the anagen phase of hair growth, thereby reducing hair loss and encouraging new growth.
Finasteride
Finasteride, or Propecia, is a prescription medication predominantly used to treat male pattern baldness. It inhibits the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which converts testosterone to DHT, which causes hair shrinkage. By reducing DHT levels, finasteride helps decrease hair loss and, in some cases, triggers hair regrowth.
Studies show that finasteride can significantly halt the progression of hair loss and lead to regrowth in many cases.
Dutasteride
Dutasteride, like finasteride, is an inhibitor of the 5-alpha reductase enzyme. However, dutasteride is more potent and inhibits type I and type II forms of the enzyme. This mechanism of action leads to a more significant reduction in DHT levels.
While traditionally available as an oral medication, particularly for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia, topical dutasteride has gained popularity for treating hair loss. The topical application reduces systemic side effects associated with oral dutasteride.
Topical dutasteride is relatively new compared to finasteride. However, early studies and clinical reviews suggest it may be more effective in reducing scalp DHT levels and promoting hair regrowth. Its dual inhibition of both types of 5-alpha reductase could offer a more robust intervention for hair loss.
Hair transplant surgery
Follicular unit transplantation and follicular unit extraction are the main types of hair transplant surgery involving hair follicle extraction. The procedure includes removing hair follicles from a healthy site and transplanting them to the balding or recipient site. Both methods can restore hair to areas significantly affected by baldness with natural-looking results.
Scalp reduction
Scalp reduction is a less common form of surgery for hair loss. It involves removing non-hair-bearing skin from the scalp, allowing the hair-bearing skin to be stretched to fill in the bald area of the head. However, this method is generally used in cases of extreme hair loss.
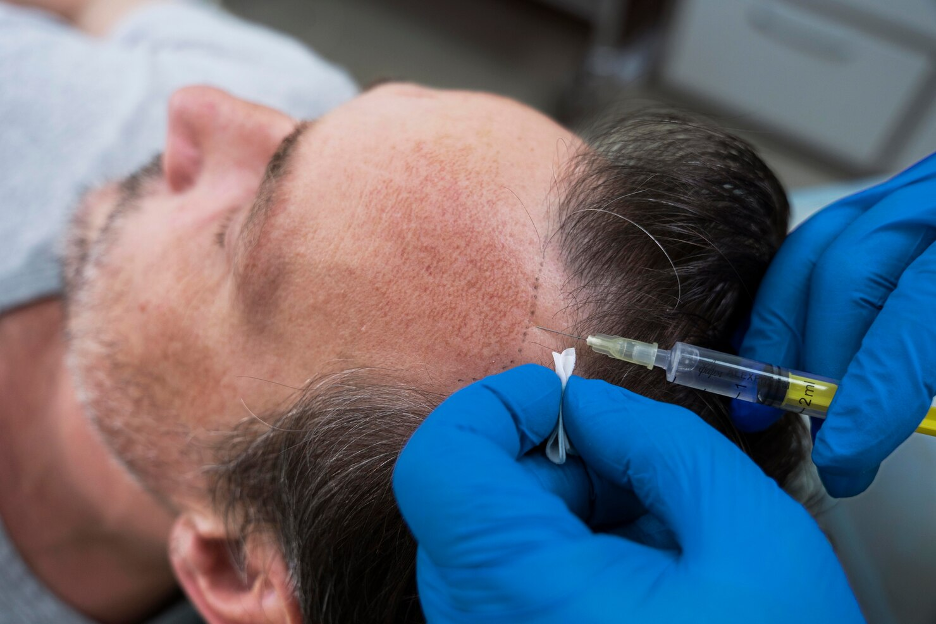
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP)
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy leverages the natural growth factors and proteins present in the blood to facilitate hair growth and scalp health. The process begins with drawing a small amount of the patient's blood. It undergoes centrifugation to separate the platelets and plasma from the other blood components. This concentrated platelet-rich plasma goes directly into the affected area at the level of the hair follicles.
The platelets in PRP release growth factors that have several roles:
- stimulating the proliferation of hair follicle cells
- prolonging the growth phase
- increasing blood supply to the hair follicles
All these help rejuvenate existing follicles and activate dormant follicles to begin growing hair again.
PRP is effective for treating hair loss primarily because it enhances the nutrient supply to the hair follicle. This process is critical to sustaining hair growth and increasing hair shaft size. By addressing hair follicle health at a cellular level, PRP can lead to noticeable improvements in hair density and thickness. Often, the therapy does not require daily medication or invasive surgery.
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT)
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) for hair loss involves using specific light wavelengths to stimulate cellular activity in the hair follicles. This therapy uses photons to penetrate the scalp and be absorbed by the mitochondria in the cells of the hair follicle. This absorption promotes increased cellular energy production, often referred to as photobiomodulation.
The enhanced cellular energy improves the metabolic activity within the hair follicles. This activity encourages the hair to shift from the telogen (resting) phase to the anagen (growth) phase.
Additionally, LLLT can increase blood flow, which brings more nutrients and oxygen to the follicles.
Studies have shown that regular use of LLLT can result in increased hair density and a slowdown in hair loss. The therapy's non-invasive nature and ease of use are often available through handheld devices or salon treatments. This accessibility makes it a preferred choice for those seeking an alternative or supplementary treatment to traditional hair loss medications.
Lifestyle and nutritional factors
Various lifestyle and nutritional factors significantly influence hair health. A well-balanced diet, regular physical activity, and effective stress management can profoundly affect hair growth and overall scalp health.
Hair is primarily made of keratin, a fibrous protein. Hence, a sufficient protein intake is crucial for hair growth. Protein deficiencies can lead to weak, brittle hair or slowing growth.
Similarly, iron is vital for producing hair cell protein, and its deficiency is one of the leading causes of hair loss. Ensuring adequate iron levels can support hair growth and prevent anaemia-related hair loss.
Zinc is vital for hair tissue growth and repair. It also maintains the oil glands surrounding the follicles working properly. However, zinc deficiency can lead to hair shedding.
When it comes to vitamins, the following offer promising results:
- Biotin (Vitamin B7): Often promoted as a hair growth supplement, biotin is involved in the production of keratin in the body. As such, it can improve hair health, leading to thicker, more resilient hair strands.
- Vitamin D: Alopecia can occur due to vitamin D deficiency. Studies show that Vitamin D promotes the creation of new follicles where new hair can grow.
Tips for Choosing the Right Treatment

Image by Freepik
Choosing the proper treatment for hair loss can be overwhelming, especially the vast array of options available. Here are some essential tips to help guide you in selecting the most appropriate and effective treatment for your specific situation:
Understand the cause of hair loss
Before choosing a treatment, it's crucial to identify the underlying cause of your hair loss. Androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, or alopecia areata are different types of hair loss, and each requires specific treatment approaches. A dermatologist or a trichologist can help you get a proper diagnosis of the factors contributing to your hair loss.
Set realistic expectations
It's important to have realistic expectations about treatment outcomes. Understand that most treatments take time to show results and may not restore your hair to its original density. Also, some treatments require ongoing commitment to maintain the effects.
Consider your lifestyle
Choose a treatment that fits well with your lifestyle. For example, if you prefer a low-maintenance approach, you might opt for a once-daily medication. Some treatments may require frequent clinic visits or complex care at home.
Evaluate safety and side effects
Research the potential side effects of each treatment option. While medications like finasteride and minoxidil are effective, they can have side effects that might not be acceptable for everyone. Similarly, surgical options carry risks of complications. Make sure you are comfortable with these risks before proceeding.
Assess the long-term commitment
Some treatments, especially medical ones, may require a long-term or lifelong commitment. Stopping these treatments could lead to a reversal of results. Understand the duration of the treatment and what it entails over the long term.
Consider budget
Cost is a significant factor when choosing a hair loss treatment. Surgical options can be expensive and are not usually covered by insurance. On the other hand, over-the-counter therapies might be more budget-friendly but less effective. Determine what you are willing to spend and explore options within your budget.
Look for clinical evidence
Opt for treatments backed by strong clinical evidence. Do due diligence and research studies and clinical trials. These evidence-based results can provide insights into treatments' efficacy and safety. Remember, reliable treatments should have data supporting their claims.
Explore combination therapies
Sometimes, a combination of treatments works better than a single approach. Discuss with your healthcare provider whether a combination of therapies might offer better results for your type of hair loss.
Seek professional guidance
Always consult with a healthcare professional who specialises in treating hair loss. They can give personalised and evidence-based advice based on your hair loss type, health history, and treatment preferences.
Explore Your Options
Image by Freepik
If you're experiencing hair loss, remember that you have several options that you can consider. Effective treatment starts with understanding the underlying cause of your hair loss, followed by a tailored treatment plan. With the right approach, many people find that they can significantly slow the progression of hair loss and, in many cases, stimulate regrowth.
This article is part of the HealthManagement.org Point-of-View Programme.
References:
- Hirose A, Terauchi M, Odai T, Fudono A, Tsurane K, Sekiguchi M, Iwata M, Anzai T, Takahashi K, Miyasaka N. Investigation of exacerbating factors for postpartum hair loss: a questionnaire-based cross-sectional study. Int J Womens Dermatol. Published online June 16, 2023. doi: 10.1097/JW9.0000000000000084
- Sibbald C. Alopecia Areata: An Updated Review for 2023. J Cutan Med Surg. Published online June 20, 2023. doi: 10.1177/12034754231168839
- Hughes, E.C. and Saleh, D. (2023) 'Telogen Effluvium', in StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430848/. (Accessed May 1, 2024)
- Ashique, S., Sandhu, N.K., Haque, S.N. et al. A Systemic Review on Topical Marketed Formulations, Natural Products, and Oral Supplements to Prevent Androgenic Alopecia: A Review. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. Published online October 4, 2020. Doi: 10.1007/s13659-020-00267-9
- Zito, P.M., Bistas, K.G. & Syed, K. (2022) 'Finasteride', in StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513329/. (Accessed May 1, 2024)Estill MC, Ford A, Omeira R, Rodman M. Finasteride and Dutasteride for the Treatment of Male Androgenetic Alopecia: A Review of Efficacy and Reproductive Adverse Effects. Georgetown Medical Review. Published online October 27, 2023. doi:10.52504/001c.88531Pillai, Jisha K; Mysore, Venkataram. Role of Low-Level Light Therapy (LLLT) in Androgenetic Alopecia. Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery. Published online Oct–Dec 2021. doi: 10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_218_20
- Vitamin D Deficiency and Hair Loss: A Case Report and Review of the Literature for Diagnosis and Treatment. Hair Transplant Forum International, July/August. Available at: https://www.ishrs-htforum.org/content/32/4/113. (Accessed May 1, 2024).





