Physicians have long used MRI to detect cancer, but results of a study in California describe the potential use of RSI as an imaging biomarker that enhances the ability to differentiate aggressive prostate cancer from low-grade or benign tumours and guide treatment and biopsy.
"Noninvasive imaging is used to detect disease, but RSI-MRI takes it a step further," said David S. Karow, MD, PhD, assistant professor of radiology at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and the study's senior author. "We can predict the grade of a tumour sometimes without a biopsy of the prostate tissue. This is taking all that's good about multi-parametric MRI and making it better."
The addition of restriction spectrum imaging (RSI) to a pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) added between 2.5 to 5 minutes to scanning time making it a fast and highly accurate tool with decreased risk compared to contrast MRI which involves injecting patients with dye, said Karow.
In the study, published online June 1 in Clinical Cancer Research, the authors said RSI-MRI corrects for magnetic field distortions found in other imaging techniques and focuses upon water diffusion within tumor cells that exhibit a high nuclear volume fraction. By doing this, the ability of imaging to accurately plot a tumour's location is increased and allows for differentiation between tumour grades. The higher the grade, the more aggressive the cancer. Patients can have more than one tumour with different grades, however. Karow said RSI-MRI can be used to guide treatment or biopsy to target the region of highest-grade cancer.
An early diagnosis of prostate cancer typically improves a patient's prognosis. According to the National Cancer Institute, prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in men in the United States, with more than 26,000 estimated deaths this year and 180,890 new diagnoses predicted. The average age at the time of diagnosis is 66.
At UC San Diego Health, more than 1,000 patients have been imaged with RSI-MRI since 2014 and a subset have subsequently undergone MR-fused ultrasound guided prostate biopsy, said J. Kellogg Parsons, MD, MHS, UC San Diego School of Medicine associate professor of surgery and study co-author.
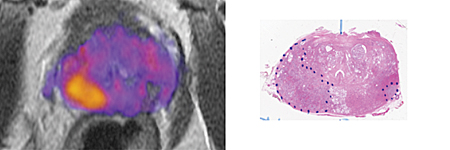
The image on the left is a magnetic resonance image (MRI) of a prostate enhanced with restriction spectrum imaging (RSI). Higher grade tumor is indicated by orange and yellow. The image on the right is a digitized section of the prostate with the tumors outlined with blue dotted lines.
"Previously, we relied completely on systematic -- but random -- biopsies of the prostate to diagnose cancer, which has been the standard practice in our field for years. Now, we use RSI-MRI to precisely target specific areas of concern and enhance the accuracy of our diagnosis," said Parsons, surgical oncologist at Moores Cancer Centre at UC San Diego Health.
"Greater accuracy means improved care tailored to each individual patient. With RSI-MRI, we are better able to identify which cancers are more aggressive and require immediate treatment, and which ones are slow growing and can be safely observed as part of a program called active surveillance."
Although this study focused on ten patients, more than 2,700 discrete data points were evaluated. Next steps include introducing the technology to other hospitals and to study whether it can be used in isolation from other screening tools. In prior papers published in the journals Abdominal Radiology and Prostate Cancer Prostatic Diseases, the same authors reported that RSI-MRI increases detection capability and can perform better than traditional multi-parametric MRI when used in isolation.
These data suggest that RSI-MRI could eventually serve as a stand-alone, non-contrast screening tool that would take 15 minutes compared to a normal contrast-enhanced exam lasting 40 to 60 minutes.
Anders Dale, PhD, professor of radiology and neurosciences and co-director of the Multimodal Imaging Laboratory at UC San Diego, and Nate White, PhD, assistant professor of radiology, initially co-invented RSI-MRI to characterise aggressive brain tumours.
"RSI-MRI could be a transformational imaging technology for oncologists in the same way CT scans altered the way effects of treatment are quantitated from plain X-rays," said Jonathan W. Simons, MD, Prostate Cancer Foundation president and Chief Executive Officer. "Based on the investigations at UC San Diego, this is a particular promise that needs more validation. Now testable is the hypothesis that RSI-MRI could identify oligometastatic prostate cancer that became curable through its identification by RSI-MRI."
Source:
University of California, San Diego Health Sciences
Journal Reference:
G. Yamin, N. M. Schenker-Ahmed, A. Shabaik, D. Adams, H. Bartsch, J. Kuperman, N. S. White, R. A. Rakow-Penner, K. McCammack, J. K. Parsons, C. J. Kane, A. M. Dale, D. S. Karow. Voxel Level Radiologic-Pathologic Validation of Restriction Spectrum Imaging Cellularity Index with Gleason Grade in Prostate Cancer. Clinical Cancer Research, 2016; 22 (11): 2668 DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2429



























